Periodontal Disease
Preventing Gum Disease
Causes of Periodontal Disease
Types of Periodontal Disease
Preventing Gum Disease
Don’t Ignore Your Oral Health
Periodontal Care
Periodontal treatment is necessary when various conditions
affect the health of your gums and the regions of your jawbone which hold your
teeth in place. Retaining your teeth is directly dependent on proper
periodontal care and maintenance (follow-up care). Healthy gums enhance the
appearance of your teeth, like a frame around a beautiful painting. When your
gums become unhealthy, they can either recede or become swollen and red. In
later stages, the supporting bone is destroyed and your teeth will shift, loosen
or fall out. These changes not only affect your ability to chew or speak; they
can affect your overall health as well as spoil your smile.

Periodontal Disease
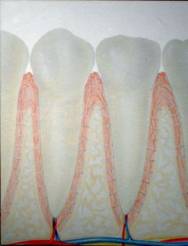
Healthy
Periodontal (gum
diseases), including gingivitis and periodontitis, are serious infections that,
left untreated, can lead to tooth loss. The word periodontal literally means
“around the tooth”. Periodontal disease is a chronic bacterial infection that
affects the gums and bone supporting the teeth. Healthy gum tissue consist of
strong fibers which give the tissue its characteristic light pink color. The
primary objective of this tissue is to protect the bone and root of the tooth
from the oral environment, especially from bacteria getting under the tissue and
establishing an infection.
Periodontal
disease can affect one tooth or many teeth. It begins when the bacteria in
plaque (the sticky, colorless film that constantly forms on your teeth) causes
the gums to become inflamed.
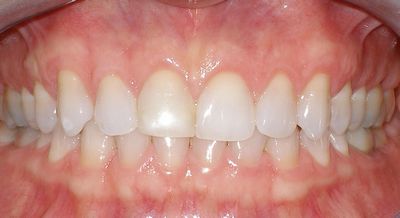
In the mildest form
of the disease, gingivitis, the gums redden,
swell and bleed easily. There is usually little or no discomfort. Gingivitis
is often caused by inadequate oral hygiene. Gingivitis is reversible with
professional treatment and good oral home care.
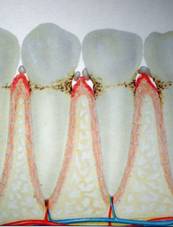
Gingivitis
Untreated
gingivitis can advance to periodontitis. With
time, plaque can spread and grow below the gum line. Toxins produced by the
bacteria in plaque irritate the gums. The toxins stimulate a chronic
inflammatory response in which the body in essence turns on itself, and the
tissues and bone that support the teeth are broken down and destroyed. Gums
separate from the teeth, forming pockets (spaces between the teeth and gums)
that
become infected.
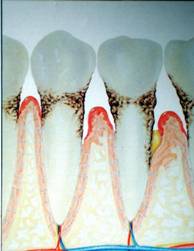
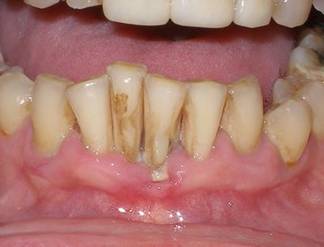
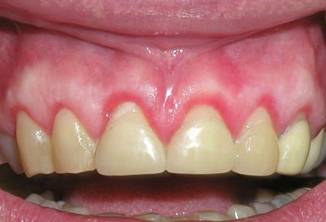
Periodontitis
Untreated
periodontal disease will advance with time leading to
advanced periodontitis. As the disease progresses, the pockets deepen
and more gum tissue and bone are destroyed. Often, this destructive process has
very mild symptoms. Eventually, teeth can become loose and may have to be
removed.
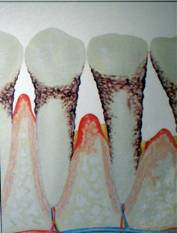
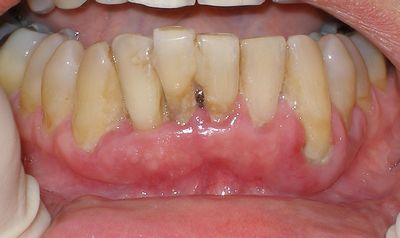
Advanced Periodontitis

Causes of Periodontal Disease
The main cause of
periodontal disease is bacterial plaque, a sticky, colorless film that
constantly forms on your teeth. However, factors like the following also affect
the health of your gums.
Smoking/Tobacco Use
Tobacco users also
are at increased risk for periodontal disease. In fact, recent studies have
shown that tobacco use may be one of the most significant risk factors in the
development and progression of periodontal disease.
Genetics
Research proves
that up to 30% of the population may be genetically susceptible to gum disease.
Despite aggressive oral care habits, these people may be six times more likely
to develop periodontal disease.
Pregnancy and Puberty
As a woman, you
know that your health needs are unique. You know that brushing and flossing
daily, a healthy diet, and regular exercise are all important to help you stay
in shape. You also know that at specific times in you life, you need to take
extra care of yourself. Times when you mature and change, for example, puberty
or menopause, and times when you have special health needs, such as menstruation
or pregnancy. During these particular times, your body experiences hormonal
changes. These changes can affect many of the tissues in your body, including
your gums. Your gums can become sensitive, and at times react strongly to the
hormonal fluctuations. This may make you more susceptible to gum disease.
Additionally, recent studies suggest that pregnant women with gum disease are
seven times more likely to deliver preterm low birth weight babies.
Stress
As you probably
already know, stress is linked to may serious conditions such as hypertension,
cancer, and numerous other health problems. What you may not know is that
stress also is a risk factor for periodontal disease. Research demonstrates
that stress can make it more difficult for the body to fight off infection,
including periodontal disease.
Medications
Some drugs, such as
oral contraceptives, anti-depressants, high blood pressure medicine and certain
heart medicines, can affect your oral health. Just as you notify your
pharmacist and other health care providers of all medicines you are taking and
any changes in your overall health, you should also inform your dental care
provider.
Clenching or Grinding Your Teeth
Has anyone ever
told you that you grind your teeth at night? Is your jaw sore from clenching
your teeth when you’re taking a test or solving a problem at work? Clenching or
grinding your teeth can put excess force on the supporting tissues on the teeth
and could speed up the rate at which these periodontal tissues are destroyed.
Diabetes
Diabetes is a
disease that causes altered levels of sugar in the blood. According to the
American Diabetes Association, approximately 16 million Americans have diabetes;
however, more than half have not been diagnosed with this disease. If you are
diabetic, you are at higher risk for developing infections, including
periodontal diseases. These infections can impair the ability to process and/or
utilize insulin, which may cause your diabetes to be more difficult to control
and your infection to be more severe than a
non-diabetic.
Poor Nutrition
As you may already
know, a diet low in important nutrients can compromise the body’s immune system
and make it harder for the body to fight off infection. Because periodontal
disease is a serious infection, poor nutrition can worsen the condition of your
gums.

Types
of Periodontal Disease
There are many
forms of periodontal disease. The most common ones include the following:
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is the
mildest form of periodontal disease. It causes the gums to become red, swollen,
and bleed easily. There is usually little or no discomfort at this stage.
Gingivitis is reversible with professional treatment and good home care.
Aggressive Periodontitis
A form of
periodontitis that occurs in patients who are otherwise clinically healthy.
Common features include rapid attachment loss and bone destruction and familial
aggregation.
Chronic Periodontitis
A form of
periodontal disease resulting in inflammation within the supporting tissues of
the teeth, progressive attachment and bone loss and is characterized by pocket
formation and/or recession of the gums. It is recognized as the most frequently
occurring form of periodontitis. It is prevalent in adults, but can occur at
any age. Progression of attachment loss usually occurs slowly, but periods of
rapid progression can occur.
Necrotizing Periodontal Disease (“Trench Mouth”)
An infection
characterized by necrosis of gingival tissues, periodontal ligament and bone.
These lesions are most commonly observed in individuals with poor oral hygiene
and malnutrition.

Preventing
Gum Disease
Adults past the age
of 35 lose more teeth to gum diseases than from cavities. Three out of four
adults are affected at some time in their life. The best way to prevent
cavities and periodontal diseases is by good tooth brushing and flossing
techniques, performed daily, coupled with regular professional examinations and
cleanings. Unfortunately, even with the most diligent home dental care, people
still can develop some forms of periodontal disease. Once this disease starts,
professional intervention is necessary to prevent its progression.
Other important
factors that negatively affect the health of you gums include:
- tobacco
usage
- diabetes
- stress
- clenching
and grinding teeth
- some
medications
- poor
nutrition

Don’t Ignore Your Oral Health
If you value your
oral as well as your over all health, a periodontal evaluation is a good idea.
Sometimes the only way to detect periodontal disease is through a periodontal
evaluation. A periodontal evaluation may be especially important if you:
- Notice any
symptoms of periodontal disease (bleeding or receding gums, bad breath, etc.)
- Have heart
disease, diabetes, respiratory disease or osteoporosis.
- Are
thinking of becoming pregnant.
- Have a
family member with periodontal disease. Research suggests that the bacteria
that cause periodontal disease can pass through saliva. This means the common
contact of saliva in families puts children and couples at risk for contracting
the periodontal disease of another family member.
- Have a
sore or irritation in your mouth that does not get better with two weeks.
Visit
www.perio.org and
www.AmericanHeart.org for more information on
periodontal disease and cardiovascular health.
